What are Gastroparesis Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis?
Understand Gastroparesis Causes, Symptoms Diagnosis, and discover available treatments to evaluate the condition.
Dr. Chris Ibikunle is one of the few advanced endoscopic surgeons in the United States who performs GPOEM aka POP procedure for Gastroparesis.
Gastroparesis is a condition that causes nausea and vomiting. It can also make you feel full too soon after you start eating. It happens because the stomach takes too long to empty and does not move food along through your body fast enough. Gastroparesis is also called “delayed gastric emptying.” (Gastric” means “having to do with the stomach.)
Gastroparesis is a common problem among people with diabetes. It also can happen to people who have had food poisoning (gastroenteritis). But it can sometimes happen to people who have not been sick and who do not have diabetes.
When gastroparesis starts after someone has had food poisoning, it often gets better in a few days to weeks. Sometimes it lasts longer or never goes away. In people with diabetes, it usually does not go away, but some things can make it better.
Gastroparesis Symptoms
The symptoms can include:
- Belly pain.
- Weight loss.
- Nausea with or without vomiting.
- Feeling full too soon after you start eating.
- Bloating (feeling as though your stomach is full of air).
Gastroparesis Diagnosis
Yes. If your doctor or nurse suspects you have gastroparesis, you might do 1 or more of these tests:
1. Endoscopy
A doctor or nurse puts a thin tube down your throat and into your stomach. The tube (called an endoscope) has a light and a tiny camera on the end, so it allows the doctor or nurse to see inside your stomach. If you still find food in your stomach even though it has been more than 8 hours since you ate, that is a sign that you might have gastroparesis.
2. Barium Follow-Through, CT Scan, or MRI
For these tests, you eat a special substance that shows up on imaging. This can show if something is blocking the flow of food, keeping it from leaving your stomach.
3. Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy
For this test, you eat food that has a small amount of radioactive material in it. Then you have images taken of the inside of your body for up to 4 hours. That way, doctors can follow where the food goes and how fast it gets there. If you still have a fair amount of food in your stomach after 4 hours, that means you have gastroparesis.
Should I change my diet to feel better?
Yes. Some people feel better if they:
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
- Put food through the blender before eating it.
- Eat 4 to 5 small meals during the day instead of 2 or 3 big ones.
- Avoid fizzy drinks, like soda, as they can cause more bloating and gas.
- Cut down on foods that have a lot of fat, such as cheese and fried foods.
- Cut down on foods that have a lot of “insoluble” fiber, such as some fruits, vegetables, and beans.
If you have diabetes, it’s also very important to keep your blood sugar as close to normal as possible.
Gastroparesis Treatment?
See your doctor or nurse if you have ongoing nausea or vomiting, belly pain, trouble eating, or weight loss. Treatments can include:
- Medicines that help prevent nausea.
- Medicines that make the stomach empty faster.
- Emptying the stomach with a tube – To do this, doctors can put a tube down your throat or directly into your stomach through your skin.
- Treatments to help you get the food and fluids you need – This might include taking liquid food supplements or – in rare cases – being fed through a tube.
- Electrical stimulation of the stomach – In very rare cases and for certain causes of gastroparesis, doctors use electrical stimulation to make the stomach empty.
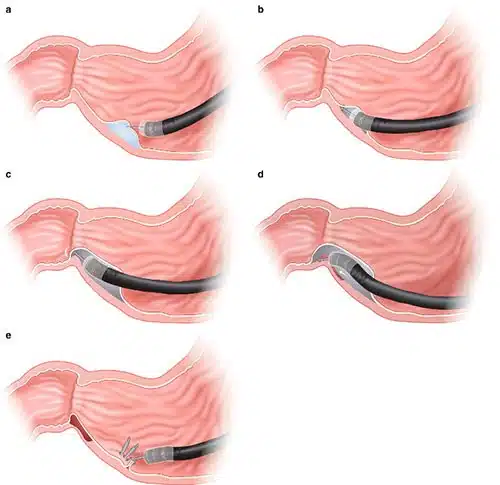
- The latest minimally invasive approach that has shown great results in improving gastric emptying is the Gastric Per Oral Endoscopic myotomy (GPOEM) aka Per Oral Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy (POP) procedure. This procedure is incisionless and is all done endoscopic. With GPOEM aka POP Procedure, your doctor cuts the pylorus muscle of the stomach to improve the emptying of food into the small bowel. Studies showed that 50% to 70% of patients will have normalization of their gastric emptying and 80% will have improvement of their symptoms.
Found Out More about Gastroparesis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Publications on GPOEM aka POP Procedure:
G Poem Information from US National Library of Medicine
POP Procedure for Gastroparesis from US National Library of Medicine
Furthermore, to choose the treatment that’s right for you, talk with your doctor. Ask him or her about the benefits, risks, and side effects of each treatment.






