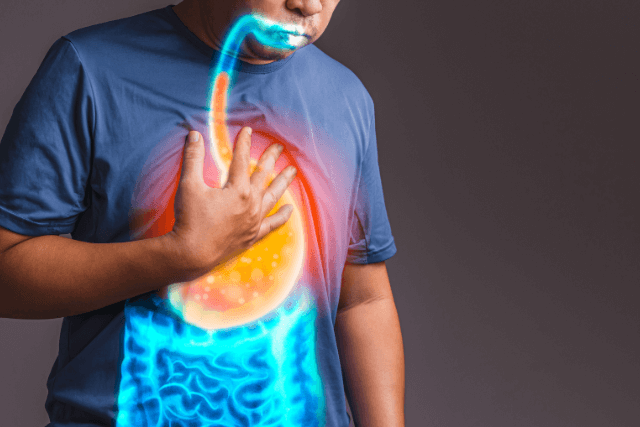
Acid reflux is a common digestive condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, acid reflux can cause discomfort and pain. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal ulcers, and even cancer in extreme cases. Understanding the symptoms of acid reflux and knowing how to manage them is essential for maintaining your digestive health and overall well-being.
In this blog, we will explore the symptoms of acid reflux, how to identify them, and various management strategies to prevent or alleviate the condition. By understanding the causes and symptoms of acid reflux, you can take proactive steps to reduce its impact on your life.
What is Acid Reflux?
Before diving into the symptoms, it’s important to understand what acid reflux is and how it affects the body. Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid or bile flows backward into the esophagus. This happens when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a valve that separates the esophagus and stomach, becomes weakened or relaxes abnormally. When the LES doesn’t close properly, stomach acid can enter the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation.
This backward flow of acid can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. Some of these symptoms are easy to spot, while others may be less obvious. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early on to prevent long-term damage to the esophagus and other digestive organs.
Common Acid Reflux Symptoms
Acid reflux symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and they may occur sporadically or on a regular basis. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in identifying and managing the condition effectively.
1. Heartburn
One of the most common and well-known symptoms of acid reflux is heartburn. Heartburn is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest, usually just behind the breastbone. This sensation occurs when stomach acid irritates the lining of the esophagus. The discomfort can worsen after eating, bending over, or lying down.
How to manage it: Heartburn is often alleviated by avoiding foods and drinks that trigger acid reflux, such as spicy foods, citrus, chocolate, and caffeine. Eating smaller meals and avoiding lying down after eating can also help.
2. Regurgitation
Another hallmark symptom of acid reflux is regurgitation, which involves the sensation of acid or food coming back up into the mouth. This can leave a sour or bitter taste in the mouth and is often accompanied by a feeling of nausea.
How to manage it: To manage regurgitation, avoid overeating, and refrain from lying down after meals. Staying upright for at least three hours after eating can reduce the risk of acid backing up into the esophagus.
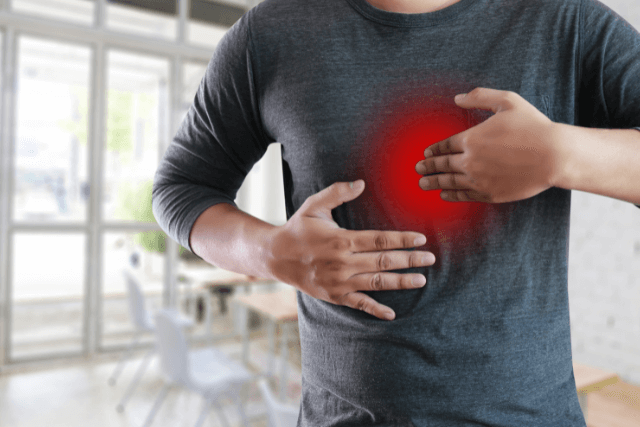
3. Chest Pain
Although chest pain can be caused by a variety of conditions, it can also be a symptom of acid reflux. This pain is often described as a sharp, burning sensation in the chest, and it can be mistaken for a heart attack. However, the pain associated with acid reflux usually occurs after eating and can be relieved by belching or taking antacids.
How to manage it: If chest pain is suspected to be related to acid reflux, managing the underlying acid production is key. In some cases, medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid.
4. Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
Acid reflux can lead to the narrowing of the esophagus, causing difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia. This occurs because the esophagus becomes irritated and inflamed due to repeated acid exposure. As the esophagus becomes narrowed, it can be more difficult for food and liquids to pass through.
How to manage it: If you’re experiencing difficulty swallowing, it’s essential to manage acid reflux with proper medication and lifestyle changes. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair damage caused by acid reflux.
5. Hoarseness or Sore Throat
Chronic acid reflux can lead to a hoarse voice or a persistent sore throat. This happens because stomach acid irritates the vocal cords and the lining of the throat. If you frequently wake up with a sore throat or notice your voice becoming hoarse, acid reflux could be the cause.
How to manage it: Staying hydrated, using a humidifier at night, and avoiding late-night meals can help alleviate throat irritation. If hoarseness persists, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment.
6. Chronic Cough
A chronic cough that doesn’t seem to go away, particularly after eating or while lying down, could be a sign of acid reflux. Acid can irritate the airways, leading to coughing and wheezing. This type of cough is often worse at night or in the morning.
How to manage it: To manage a chronic cough, avoid triggers such as smoking and certain foods. Taking medication to reduce acid production can also help relieve symptoms.
7. Asthma-like Symptoms
In some cases, acid reflux can trigger asthma-like symptoms, such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. This is particularly common in people who already have asthma, as acid reflux can worsen existing respiratory symptoms.
How to manage it: Managing acid reflux with medication and lifestyle changes can reduce asthma-like symptoms. If symptoms persist, your healthcare provider may suggest additional treatments.
How to Identify Acid Reflux Symptoms
Recognizing acid reflux symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. If you frequently experience heartburn, regurgitation, or other symptoms of acid reflux, it may be time to seek medical attention. An early diagnosis can help prevent the progression of acid reflux into more serious conditions like GERD.
Explore potential triggers and symptoms causing discomfort with our free Online GERD Calculator. Take the Heartburn, Acid Reflux, and GERD Stage Diagnoses Quiz to assess your symptoms and gain valuable insights into the stage of your condition.
When to Seek Medical Help
If your symptoms are frequent or severe, or if they interfere with your daily life, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. In some cases, acid reflux can cause damage to the esophagus, leading to complications like esophageal ulcers, bleeding, or strictures. A doctor can perform tests such as an endoscopy or pH monitoring to determine the severity of your condition.
Managing Acid Reflux Symptoms
Once you’ve identified the symptoms of acid reflux, the next step is to manage them. There are various lifestyle changes and treatments available to help reduce acid reflux symptoms and improve your quality of life.

1. Lifestyle Changes
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Instead of eating large meals, try eating smaller meals throughout the day. This can reduce pressure on the stomach and prevent acid reflux.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Certain foods and beverages can trigger acid reflux, such as spicy foods, citrus, chocolate, fatty foods, and caffeine. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage your symptoms.
- Don’t Lie Down After Eating: After eating, wait at least three hours before lying down to reduce the risk of acid flowing back into the esophagus.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. Losing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce symptoms.
2. Medications
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and provide relief from mild acid reflux symptoms.
- H2 Blockers: These medications reduce the amount of acid the stomach produces. They are available over the counter or by prescription.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs are stronger medications that block acid production in the stomach. They are typically used for more severe cases of acid reflux and are available by prescription.
- Prokinetics: These medications help strengthen the LES and improve digestion, preventing acid reflux.
3. Surgery
In some cases, lifestyle changes and medications may not be enough to control acid reflux symptoms. Surgery may be recommended if the condition is severe or if other treatments have not been effective. The most common surgery for acid reflux is fundoplication, which involves wrapping the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus to prevent acid reflux.
Conclusion
Acid reflux is a common condition that can cause a range of symptoms, from heartburn and regurgitation to difficulty swallowing and chronic cough. Recognizing the symptoms early is key to managing the condition and preventing long-term damage to the esophagus. By making lifestyle changes, using medications, and seeking medical treatment when necessary, you can effectively manage acid reflux and improve your quality of life.
If you experience frequent or severe acid reflux symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment. With the right management, you can keep acid reflux under control and maintain a healthy digestive system.