Botoxing Treatment Overview
Meet Lead Botox Injector, Stephanie Stegner. Highly trained injector and certified in Neuromodulators, Dermal fillers, and Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy. She will assess your needs, determine the best injection site or sites, and inject the Botox to get the results you want. At IBI Healthcare, precision and expertise are key to avoiding complications and natural-looking results.
But she will cover the basics to more advanced information about how Botox works. Specifically, its uses, and its importance in both cosmetic and medical fields. As well as its history, uses, and benefits.

What are Botox and Botulinum Toxins?
Botox has become a household name, but there’s more to Botox and botulinum toxin injections than that.
Specifically the brand name Botulinum toxin, made by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. To treat wrinkles and facial creases.
It’s a neurotoxin that temporarily relaxes facial muscles, and reduces the appearance of frown lines and wrinkles.
Where does it come from and what exactly does Botox do?
Notably, bacteria found in contaminated foods can also produce botulinum toxin. However, scientists extract botulinum toxin from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, freeze it, and use it later.
In medical use, the toxin first became available during clinical trials in the 1970s. Typically, plastic surgeons inject it into the eye muscle. Purified in the 1940s, it identified with eight different botulinum toxin species.
Type A has its strongest potential. Botulinum Toxin types A and C are available in several name groups. It involves botox Dysport and Xeamin. It contains botulinum toxin B (BT B) in the body. Specifically, they marketed the items as Myobloc.
Botulinum Toxin Type
What Type of Toxin is the Botulinum Toxin Injections?
Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin, one of the most potent and lethal toxins known. It inhibits the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is essential for muscle contraction.
This inhibition results in temporary muscle paralysis. That is why a Botox injection is effective in treating conditions involving muscle spasms or overactivity.
What Type of Drug is Botulinum Type A?
Type A is classified as a neurotoxin and a neuromuscular blocker. It is not only used for therapeutic but also for cosmetic applications. They are furthermore, making it a versatile drug.
Therapeutically, it treats conditions like chronic migraines, muscle spasticity, and excessive sweating. Cosmetically, it is primarily used to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles.
What Type of Toxin is C. Botulinum?
Clostridium botulinum produces several types of botulinum toxin, including types A, B, E, and F. Type A is the most commonly used for medical and cosmetic treatments. Consequently, these botulinum toxins are highly potent. Moreover, they can cause botulism, a serious illness characterized by muscle paralysis.
What is Botulinum Toxin Botox Type A?
Botox Type A refers to the specific formulation of type A used in Botox injections. It is the first and most well-known form of botulinum toxin injection, used in both therapeutic and cosmetic procedures. Botox Type A works by temporarily paralyzing muscles, which helps in reducing wrinkles and treating various medical conditions.
Is Botulinum Toxin Injection the Same as Botox?
Yes, botulinum toxin type b injections and Botox are essentially the same. Essentially, Botox is a brand name for botulinum toxin type A injections, administered through injections to achieve the desired effects. Other brands of botulinum toxin injections type A include Dysport and Xeomin, but Botox remains the most recognized.
How Does Botulinum Toxin Work?
Botulinum toxin works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contraction. When injected into targeted muscles, it prevents them from contracting, leading to temporary muscle paralysis. This muscle paralysis smooths out wrinkles in cosmetic applications and alleviates muscle-related conditions in medical treatments.
Usage and Applications
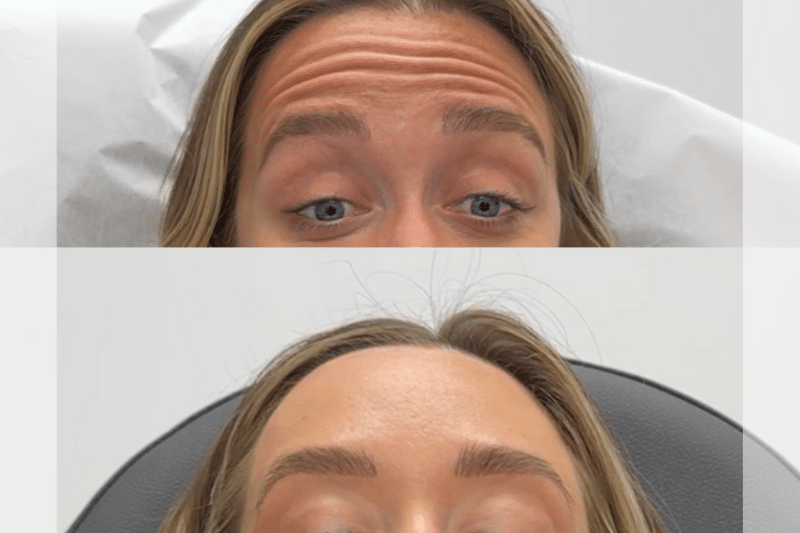
What is the Most Popular Botox Treatment?
The most popular Botox treatment focuses on reducing facial wrinkles, particularly in the upper third of the face. Botox work on:
-
Forehead – To smooth horizontal lines.
-
Crow’s Feet – Around the eyes to eliminate fine lines.
-
Glabella – Between the eyebrows to reduce frown lines.
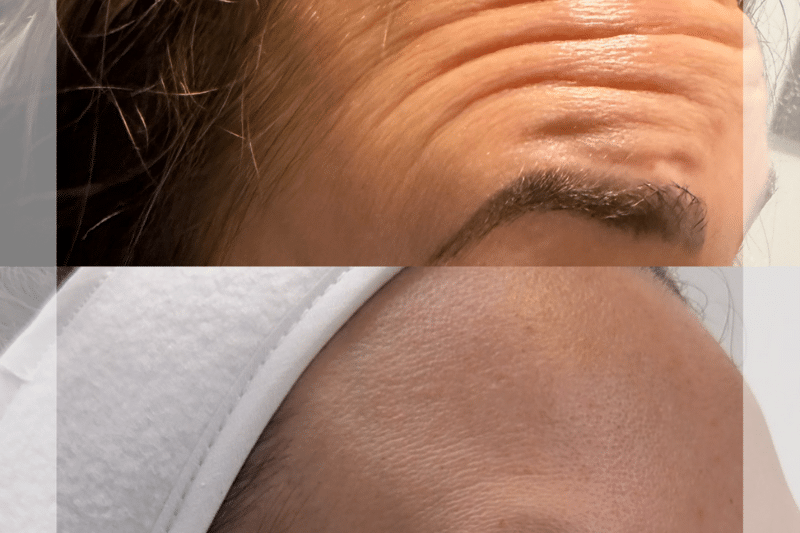
What Other Areas of the Face are Commonly Treated?
Typically, doctors inject Botox into specific muscles or facial muscles to reduce wrinkles. Common botox injection sites include:
-
Neck – To reduce neck bands.
-
Chin – To smooth a dimpled chin.
-
Bunny Lines – On the nose to reduce wrinkles.
-
Jawline – To slim the face by reducing muscle bulk.
-
Lip Lines – Around the mouth to soften the smoker’s lines.
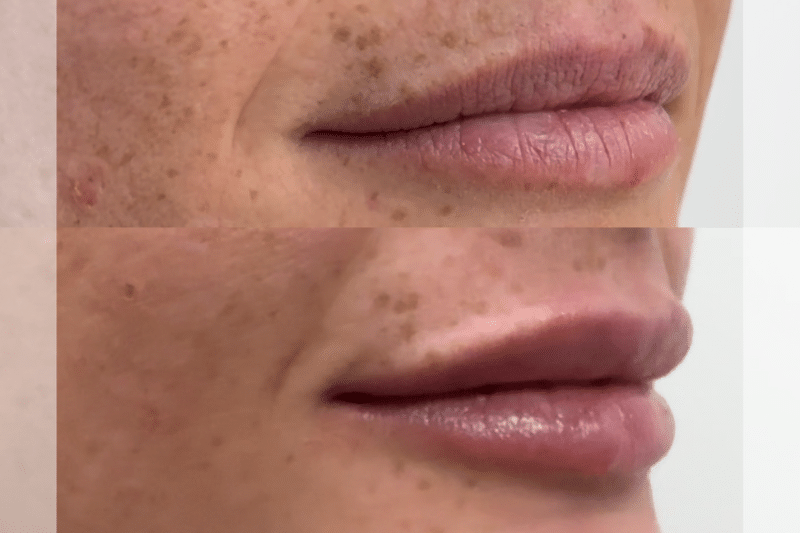
What Does Botox Injections Do to Your Face?
Botox injections temporarily paralyze targeted facial muscles, preventing them from contracting and forming wrinkles. This results in smoother, more youthful-looking skin. Additionally, Botox shots can also subtly lift certain areas of the face. For instance, specific muscles such as the eyebrows. Further providing a refreshed appearance.
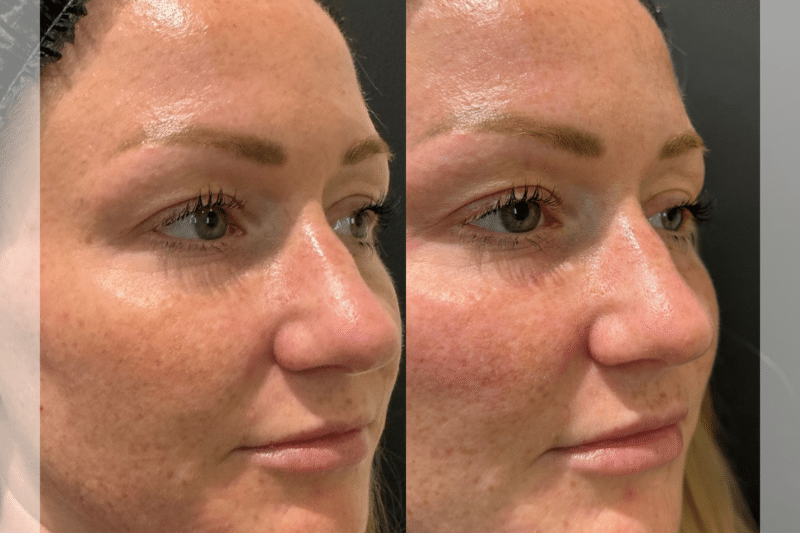
How many shots do you get?
The number of shots varies depending on the area and the results you want. However, in cosmetic applications, multiple small injections are administered in the targeted area.
For example, crow’s feet might require 5-10 shots around each eye. Whereas the forehead might require 10-20 shots across the treatment area of the forehead and glabellar region.
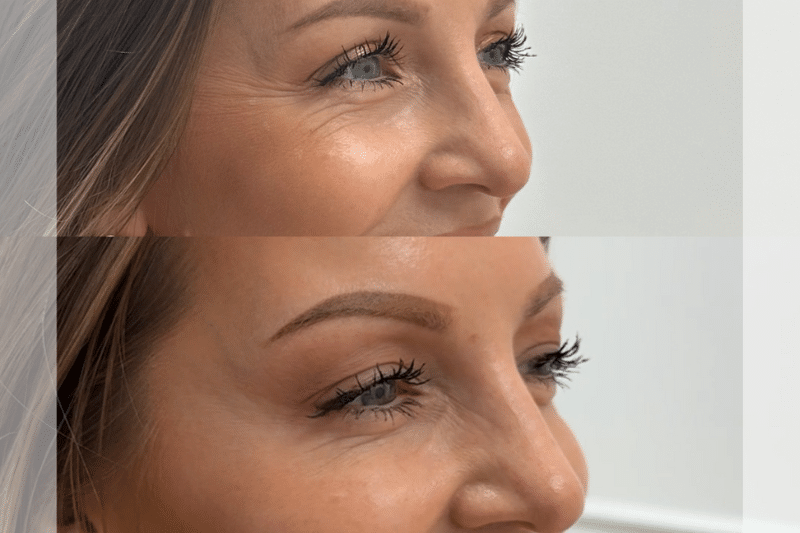

Can it be used for Medical Purposes?
Indeed, Botox use and application are not only limited to medical and cosmetic purposes. Furthermore, it treats health conditions beyond reducing cosmetic wrinkles.
-
Strabismus – Corrects crossed eyes.
-
Blepharospasm – Treats eye twitching.
-
Hyperhidrosis – Controls excessive sweating.
-
Overactive Bladder – Relieves urinary incontinence.
-
Migraines – Reduces frequency and severity of headaches.
-
Muscle Spasms – Relaxes muscles in patients with cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
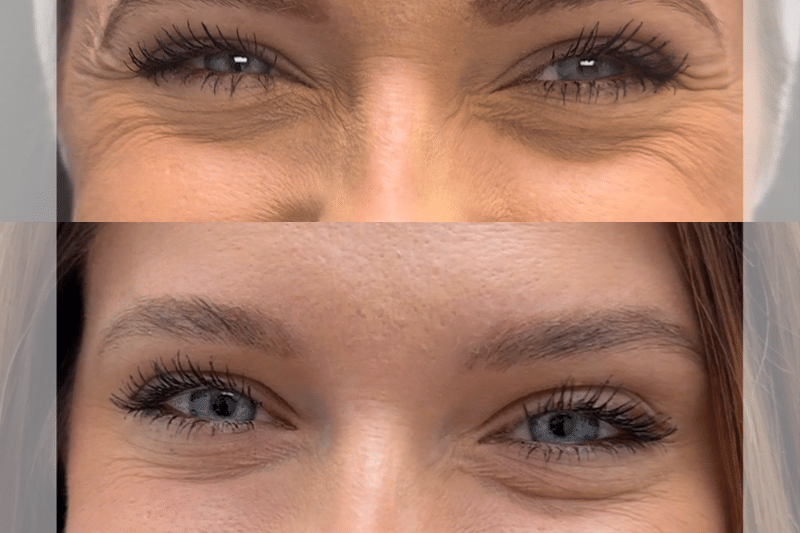
How is Botox Used for Migraine Treatment?
Moreover, Botox injections are FDA approved for treating chronic migraines in adults. It works by blocking the release of certain chemicals from nerves involved in pain transmission.
Thereby reducing the frequency and severity of the often severe neck pain during migraine attacks. Typically, doctors administer Botox injections in specific areas around the head and neck every 12 weeks for optimal painless results.
Types and Variants
What Are the 3 Types of Botox and How Do the Different Types of Botox Compare?
Several brands produce botulinum toxin for medical and cosmetic purposes and use. Botox has different types, mainly classified based on their specific formulations and brands. Each type of Botox has unique properties and benefits. The most recognized brands and primary types in the United States include:
Botox Cosmetic (OnabotulinumtoxinA)
- This is the most well-known type, commonly used for reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines. Known for its precision, it’s ideal for treating small areas like crow’s feet and forehead lines.
Dysport (AbobotulinumtoxinA)
- This type spreads more easily. Often used for larger areas such as the forehead.
Xeomin (IncobotulinumtoxinA)
- Known for its purity, Xeomin is free from complex proteins, which may reduce the risk of developing resistance. Ideal for patients who have previously used other types.
Are There Different Brands of Botulinum Toxin?
Jeuveau (PrabotulinumtoxinA-xvfs)
- A newer brand that has gained popularity for its effectiveness in treating glabellar, lines and wrinkles. Similar to Botox Cosmetic but often marketed as a more affordable option.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Different Botox Types?
Botox Cosmetic Pros:
-
Precise application.
-
Long track record of safety and effectiveness.
Botox Cosmetic Cons:
-
Higher cost compared to some other brands.
Dysport Pros:
-
Spreads easily, good for large areas.
-
Slightly faster onset of effects.
Dysport Cons:
-
Less control over the precise area, which can affect surrounding muscles.
Xeomin Pros:
-
No complex proteins, reducing the risk of resistance.
-
Often seen as a purer alternative.
Xeomin Cons:
-
May not last as long in some patients.
Jeuveau Pros:
-
Effective and often less expensive.
-
Similar results to Botox Cosmetic.
Jeuveau Cons:
-
Newer, so less long-term data is available.
Treatment Effects and Duration
How Long Do Botox Injections Last?
Botox injections typically last between three to four months. The exact duration can vary based on factors such as the patient’s age, skin condition, and the area treated.
How Long Does a Botox Shot Last?
A single Botox shot, administered in one session, lasts about the same duration—three to four months. However, some patients may notice effects starting to diminish after two months. While others may enjoy results for up to six months. Consistent treatment can sometimes extend the duration of effects as muscles become trained to relax.
What Are the Later Effects of Botox?
Over time, regular Botox treatments can lead to health problems:
-
Reduced severity of wrinkles – As treated muscles become trained to relax.
-
Finer, less pronounced lines – Continued treatment can prevent new lines from forming.
-
Potential muscle atrophy – With prolonged use, some muscles may shrink slightly, reducing their ability to create wrinkles.
What Happens When You Stop Using Botox?
If you stop using Botox, the treated muscles will gradually regain their ability to contract fully. Consequently, wrinkles and lines will slowly return to their pre-treatment state. However, stopping Botox will not make your lines and wrinkles worse than they were initially.
How Quickly Does Botox Take Effect?
Botox typically starts to take effect within three to five days after injection. Full results are usually visible within one to two weeks.
What Factors Influence the Duration of Botox Effects?
Several factors can influence how long Botox effects last:
-
Age- Younger skin tends to retain effects longer.
-
Dosage – Higher doses may provide longer-lasting results.
-
Skin Condition – Healthier skin may maintain effects better.
-
Metabolism – Faster metabolism can reduce the duration of effects.
-
Area Treated – Results in more active areas (like the forehead) may wear off faster.
How Often Should You Get Botox Treatments?
Most practitioners recommend Botox treatments every three to four months to maintain optimal results. Over time, the frequency may decrease as muscles learn to relax, and the cumulative effects of treatments take hold.
Side Effects and Safety
What Are the Common Side Effects of Botox Injections?
Botox, while widely used and generally safe, can have serious side effects too. The three most common ones include:
-
Headaches – Some patients report mild to moderate headaches post-injection.
-
Flu-like Symptoms – These can include fatigue, mild fever, and general malaise.
-
Bruising and Swelling – This often occurs at the injection site and usually resolves within a few days.
In addition to the symptoms of the common side effects, Botox injections can also cause:
-
Dry Eyes or Excessive Tearing -This occurs especially when treating the eye area.
-
Droopy Eyelids or Brows – This is usually temporary and may last a few weeks.
-
Muscle Weakness – In the injected area, leading to asymmetry in facial expressions.
-
Allergic Reactions – Though rare, symptoms can include itching, rash, or breathing difficulties.
How Long Does It Take to Feel Normal After Botox?
Most patients start to feel normal within a few days after the injection. Nonetheless, it can take up to two weeks for the full effects to appear. Similarly, for any side effects to subside. Following the aftercare instructions can speed up this process.
Who Should Not Get Botox?
Botox may not be suitable for everyone. People who should avoid Botox include:
-
Those Allergic to Botulinum Toxin – Allergies to any ingredients in Botox can cause serious reactions.
-
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women – The effects of Botox on an unborn baby or a nursing infant are not well-studied.
-
Individuals with Neuromuscular Disorders – Conditions like ALS, myasthenia gravis, or Lambert-Eaton syndrome, Botox can exacerbate these conditions.
How Toxic Is Botulinum Toxin?
Botulinum toxin is highly toxic in large amounts. However, the doses used in medical and cosmetic treatments are extremely small and controlled, making them safe for most patients. The safety of Botox treatments depends on proper administration by a qualified professional.
What Is an Example of Botulinum Toxin Poisoning?
An example of botulinum toxin poisoning is botulism, a rare but serious illness caused by large amounts of the toxin. Symptoms of food poisoning include muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, and paralysis. This condition requires immediate medical attention and is not related to cosmetic or medical Botox injections or treatments.
Are There Any Long-Term Side Effects of Botox?
Long-term side effects of the Botox shots are rare but can include:
-
Muscle Atrophy – Repeated treatments can lead to thinning of the injected muscles over time.
-
Resistance to Treatment – Some patients may develop antibodies to Botox, reducing its effectiveness.
-
Persistent Weakness – Additionally, injections that are not spaced properly can cause prolonged muscle weakness.
How Can You Minimize the Risk of Botox Side Effects?
To minimize the risk of possible side effects here, consider the following:
-
Choose a Qualified Provider – Firstly, ensure that you are getting the treatment from an experienced and licensed injector.
-
Communicate Your Medical History – Secondly, inform your provider about any existing medical conditions or allergies.
-
Follow Pre- and Post-Treatment Instructions – Lastly, adhere to the guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
Pre and Post-Treatment Care – Preparation and Procedure
When Should You Start Botox?
The ideal age to start Botox is individually dependent. Generally, people in their late 20s to early 30s start preventive treatments to minimize fine lines and wrinkles. Some people may start earlier if they have noticeable expression lines.
How Do You Get the Best Out of Botox?
Choose an injector who knows what they’re doing. Regular sessions every three to four months. Good skin care, hydration, and sun protection.
Selecting a Qualified Healthcare Provider
Importantly, you must use Botox only under the care of a licensed and skilled healthcare provider. As it is a prescription medicine.
Talk with your healthcare provider about whether the injection therapy procedure fits your needs. Then find an expert in Botox injections through a third procedure or referral from your primary care provider.
Before the Procedure
Generally, most people don’t feel much pain during the procedure. However, you may want to numb your skin beforehand. Especially if treating your palms or feet for pain, swelling, or heavy sweating.
Discuss your medical history and what medications you are on. Your healthcare provider might use one or more methods. Either reduce pain or numb the area. Such as anesthetic applied to the skin, ice, and massage, or vibration anesthesia.
How Do You Prepare for Botox?
Proper preparation for Botox can enhance results and reduce risks:
-
Hydrate – Drink plenty of water in the days leading up to your appointment.
- Avoid Blood Thinners – Aspirin or ibuprofen for at least a week before treatment to reduce bruising.
The Injection Session
Typically, medical professionals perform Botox injections in a medical office. The number of shots needed depends on the size of the treatment area and other factors. The injection session for the botulinum toxin injections is brief and focused on giving the shots with a fine needle.
Aftercare Instructions After Botox Injection Site
Aftercare is key to Botox’s success. What you should do after the treatment:
-
Avoid lying down flat. Stay upright for at least four hours.
-
Don’t apply makeup, at least for 24 hours to prevent infection.
-
Stay away from hot showers, saunas, or intense heat for 24 hours to prevent bruising.
-
Avoid rubbing or massaging the injection site for 24 hours to prevent spreading the Botox.
-
No alcohol and certain medications before and after treatment to prevent bruising.
-
Avoid intense or vigorous exercises for 24 hours to reduce bruising and swelling.
Call us or schedule a teleconsultation to discuss your aesthetic goals with Stephanie Stegner. Above all, inquire about the best-suited Botox treatment that gives you long-lasting natural-looking results.











