What Are Piles and Hemorrhoids?
Definition and Explanation of Hemorrhoids
Piles and Hemorrhoids affect millions of people worldwide. They can be uncomfortable, painful, and embarrassing for those who have them. Piles (Hemorrhoids) are swollen blood vessels that can occur inside or outside the anus and rectum. This common medical condition affects millions of people worldwide, causing a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to significant pain.
Piles and hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectal and anal area. These veins can swell due to increased pressure in the lower rectum and can cause discomfort, itching, and bleeding. The terms are often used interchangeably, although “hemorrhoids” is the medical term, “piles” is more commonly used in some areas. Rectal bleeding is a common symptom of both internal and external hemorrhoids, often noticed during bowel movements.
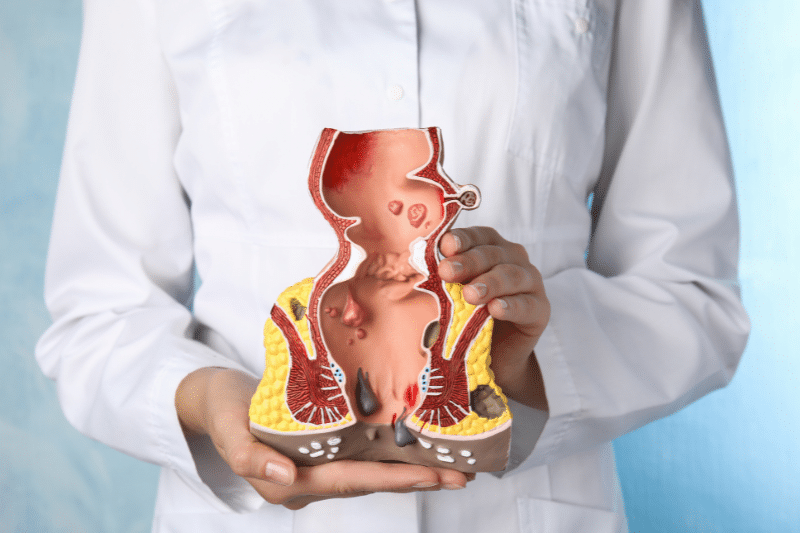
Piles and Hemorrhoids – Causes
Understanding the underlying causes of piles can help prevent the condition from recurring. Hemorrhoidal disease occurs when the supporting tissues in the rectum weaken. As a result, the blood vessels swell, leading to hemorrhoid formation.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), digestive and kidney diseases can also impact the development of hemorrhoids, emphasizing the importance of overall digestive health.
What Causes Piles?
Piles occur when the veins around the anus or lower rectum become swollen and inflamed. Several factors develop conditions including:
-
Prolonged sitting.
-
Constipation.
-
Straining.
-
Pregnancy.
-
Having extreme body weight.
-
Low fiber diet.
What Is Haemorrhoidal Tissue?
Hemorrhoidal tissue consists of blood vessels, connective tissue, and smooth muscle fibers located in the lower rectum and anus. When these tissues become inflamed, they cause piles or hemorrhoids.
What Is the Difference Between Hemorrhoids and Piles?
There’s no significant difference between being called piles and hemorrhoids; they are two names for the same condition. The term “hemorrhoid” is commonly used in the medical field, while “piles” is more informal and widely used in British English.
What Are the Risk Factors for Developing Piles?
Some of the risk factors include:
Age
Hemorrhoids are more common in older adults.
Pregnancy
Pregnant women often develop hemorrhoids due to increased pressure on the pelvic veins.
Prolonged Sitting
Sitting for long periods, especially on the same toilet paper, can lead to piles.
Studies show that approximately 40% of pregnant women experience hemorrhoids during their pregnancy, especially during the third trimester.
Can Pregnancy Cause Piles?
Yes, pregnancy is a common cause causing hemorrhoids and piles. The growing uterus increases pressure on the veins in the lower abdomen, leading to swollen veins and hemorrhoids.

Piles and Hemorrhoids – Symptoms and Identification
The symptoms of piles can vary depending on whether they are internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum, while external hemorrhoids are found under the skin around the anus.
One of the key indicators of hemorrhoids is the presence of bright red blood in the stool, on toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl.
What Do Piles Look Like?
External piles appear as lumps or swelling near the and around your anus. They may be accompanied by itching, pain, or bleeding around your anus, especially during bowel movements.
What Are the First Signs of Piles?
The first signs of piles include:
-
Itching or irritation in the anal area
-
Discomfort during bowel movements
-
Blood on toilet paper or in the toilet
-
Swelling around the anus
How Do You Check if You Have Piles?
A full physical exam and examination by a healthcare provider can confirm the presence of piles. A digital rectal exam, where a healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum, can help diagnose internal hemorrhoids and assess other rectal issues. In some cases, a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy may be required to rule out other conditions like colorectal cancer.
Do Hemorrhoids Go Away on Their Own?
Yes, mild hemorrhoids can often be managed with lifestyle changes like increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding prolonged sitting. These measures help soften stools and reduce straining during bowel movements.
For more severe cases, treatments may include over-the-counter creams, prescription medications, or medical procedures such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or surgery (hemorrhoidectomy). If symptoms persist, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate care.

Piles and Hemorrhoids – Causes – Treatment and Management
There are several alternative treatments and ways to manage and treat hemorrhoids, home treatments ranging from home remedies and topical treatments to surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the hemorrhoids.
Consulting a health care provider is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
How Do They Treat External Piles?
External piles can be treated with over-the-counter creams, warm sitz baths, and pain relief medications. Moreover, in more severe cases, medical procedures such as rubber band ligation or hemorrhoidectomy may be necessary.
According to the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS), about 10% of people with hemorrhoids require surgery. Rubber band ligation is one of the most commonly used surgical treatments for internal hemorrhoids and has a success rate of about 80%.
What Is the Best Treatment for Piles?
The best treatment for piles depends on the severity of the condition:
Mild Piles
Dietary changes, such as increasing fiber and water intake, can help.
Moderate Piles
Over-the-counter creams and suppositories can provide relief.
Severe Piles
Medical treatments like rubber band ligation or surgery may be necessary. Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids, which protrude from the anus, may require surgical treatments such as hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy.
What Shrinks Hemorrhoids Immediately?
Cold compresses, anti-inflammatory creams, and warm sitz baths can help shrink hemorrhoids and provide immediate relief from discomfort.
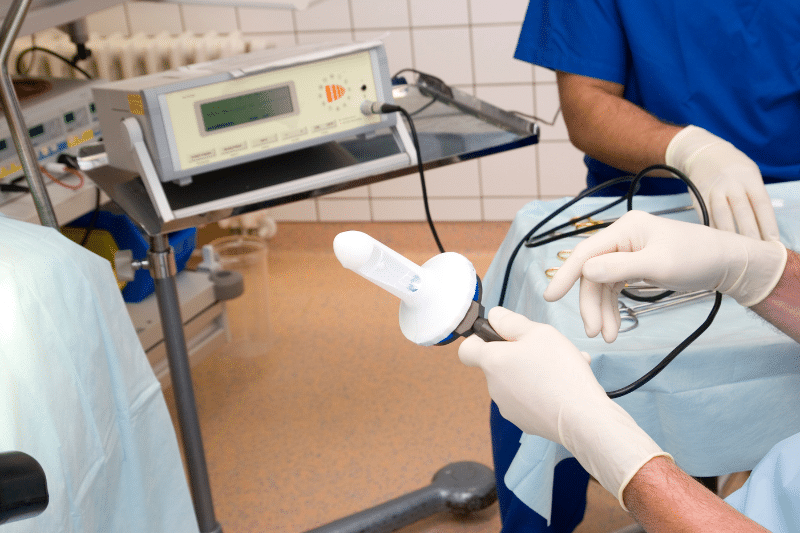
What Is Haemorrhoidal Artery Ligation?
Haemorrhoidal artery ligation is a minimally invasive medical procedure, that involves tying off the blood vessels supplying the hemorrhoid swollen blood vessels. Furthermore, this reduces the blood supply and flow to the hemorrhoid tissue, causing scar tissue around it to shrink and eventually disappear. Besides this, LHP® Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty is another minimally invasive laser procedure option.
What Are the Best Home Remedies for Hemorrhoids?
Some effective home remedies for hemorrhoids include:
Warm Sitz Baths
Sitting in warm water, known as a sitz bath, for 10-15 minutes several times a day can indeed help alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and promote healing for hemorrhoids. This simple treatment improves blood flow to the affected area, helping to soothe irritation and discomfort. It’s an effective home remedy only for mild hemorrhoids and can be done after bowel movements to provide additional relief.
Cold Compresses
Applying cold packs to the affected area can reduce swelling and discomfort.
Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe the irritation caused by hemorrhoids.

Piles and Hemorrhoids – Duration and Progression of Piles
Hemorrhoids can last for varying lengths of time, depending on their severity and the previous treatment. In many cases, mild pain resolves on its own within a few days or weeks, but severe cases may persist and require medical intervention.
How Long Do Piles Usually Last?
Mild piles may last a few days to a week, while more severe hemorrhoids can persist for weeks or even longer if left untreated.
Do Hemorrhoids Ever Fully Go Away?
Yes, hemorrhoids can go away completely with proper treatment. However, the reoccurrence happens if the underlying causes are not managed properly.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, about 50% of people who develop hemorrhoids will experience them again within five years if lifestyle changes are not made.
Is It OK to Leave Piles Untreated?
Leaving piles untreated can lead to complications, such as:
-
Chronic pain.
-
Persistent bleeding.
-
Infections In severe cases, untreated hemorrhoids can result in anemia due to blood loss.
Can Piles Reoccur After Treatment?
Yes, piles can reoccur after treatment, especially if the underlying causes not addressed. However, preventative measures, such as increasing fiber intake and avoiding prolonged sitting, can reduce the risk of recurrence.
Internal and External Hemorrhoids – Differences and Similarities
What is the Difference Between External Hemorrhoids and Piles?
External Hemorrhoids are under the skin around the anus and cause more severe pain, and discomfort. While, internal Hemorrhoids are inside the rectum and may not cause extreme pain, but can cause bleeding during bowel movements.
What is a Stage 3 Internal Hemorrhoid?
A Stage 3 internal hemorrhoid has prolapsed out of the anus but can still be pushed back in. Treatment may be rubber band ligation or surgery.
How to Prevent Piles and Hemorrhoids From Coming Back?
Preventing piles means making lifestyle changes to reduce pressure on the veins around the anus and rectum. Also, include the following in your daily routine:
-
Eat a high-fiber diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Drink plenty of water.
-
Don’t strain during bowel movements.
-
Exercise regularly.
Will Internal Hemorrhoids Go Away?
Internal hemorrhoids can resolve on their own with lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber and water intake. If they prolapse or become more severe, then medical treatments may required.
How to Get Rid of Internal Hemorrhoid Lumps?
Doctors treat internal and external hemorrhoid lumps with over-the-counter treatments. Furthermore, in some cases, doctors perform medical procedures such as rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy.

Piles and Hemorrhoids FAQs
Can You Still Poop With Piles?
Yes, you can still have bowel movements with piles. However, in case of swollen or prolapsed hemorrhoids then they are uncomfortable or painful.
Where Are Piles Placed?
Piles are located in the rectum and around your anus. Internal piles are found inside the rectum, while external piles form under the skin around the anus.
What’s the Difference Between Thrombosed Hemorrhoids and Regular Hemorrhoids?
A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when a blood clot forms inside a hemorrhoid, causing increased pain and swelling. Regular hemorrhoids may cause discomfort and bleeding but typically don’t involve clotting.
How Do You Relieve Pain from Internal Hemorrhoids?
Warm sitz baths relieve the pain from internal hemorrhoids. As well as using over-the-counter creams or suppositories, and making dietary changes also help. To further avoid chronic constipation again. However, in severe cases, doctors recommend medical treatments.
Can Over-the-counter Treatments Cure Hemorrhoids?
Over-the-counter treatments can provide relief from most hemorrhoid symptoms, but they may not cure the condition entirely. For persistent or severe hemorrhoids, medical intervention may be necessary.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology reports that hemorrhoids affect around 4.4% of the global population, with higher rates in individuals aged 45 and older.
For individuals dealing with the symptoms of hemorrhoids or even hernias, it’s essential to seek professional medical advice and make necessary lifestyle changes to prevent future occurrences prevent hemorrhoids. Lastly, with the right and timely diagnosis, hemorrhoids are treatable and manageable.











