According to the CDC, over 42% of the United States adult population is considered higher weight with a BMI of 30 or more. Individuals who battle obesity often try many diets and weight loss methods but most are ineffective long-term. When all these methods fail, the best alternative to aid in long-term weight loss is bariatric surgery. Today we are comparing the duodenal switch vs. sleeve.
Two surgery options available are gastric sleeve surgery and duodenal switch surgery. Both are effective in helping patients lose a substantial amount of weight, but is the duodenal switch the same as the gastric sleeve? If not, when should gastric sleeve surgery be used, and when should the duodenal switch be used? Furthermore, to gain a deeper understanding, continue reading to discover additional information regarding each procedure. In addition, you will learn about the distinctions between them as well as some pros and cons.
Gastric Sleeve Surgery Overview
Gastric sleeve surgery, also called sleeve gastrectomy surgery, is an effective bariatric procedure that helps high-weight patients achieve sustainable long-term weight loss.
In surgery, a surgeon accesses the stomach laparoscopically through several small abdominal incisions. Then, they proceed to cut away about 80% of the patient’s stomach and remove it.
The remainder of the stomach is stapled back together along the edge to form a sleeve-like tube that is shaped similarly to a banana. The surgery works for weight loss in two ways:
- The patient will no longer be able to consume the same amount of food during a meal because of the smaller stomach size.
- The smaller stomach fills up faster and takes longer to digest what is eaten, and therefore the patient feels “full” for a longer time.
Duodenal Switch Surgery Overview
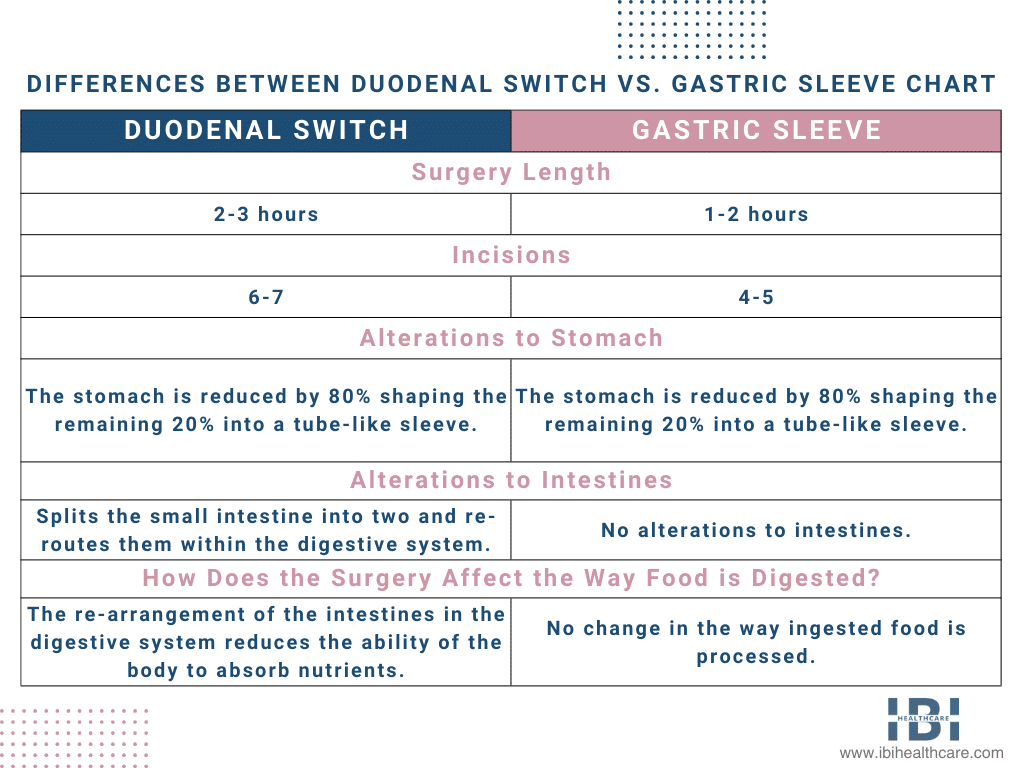
The duodenal switch is the common name for biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS). It is a more complex surgery that begins with gastric sleeve surgery but also involves re-routing the intestines.
Firstly, the stomach undergoes a procedure similar to gastric sleeve surgery. Then, the surgeon makes the stomach smaller using the same technique as gastric sleeve surgery and then divides the small intestines at the location within the small intestine responsible for dispensing the digestive enzymes (duodenum). Additionally, they strategically re-attach both sections of the small intestine to minimize the number of calories that can be absorbed and improve the digestive ability of gastric juice.
How Does Duodenal Switch Compare to Gastric Sleeve?
Pros and Cons of Duodenal Switch vs. Gastric Sleeve Chart
| Gastric Sleeve | Duodenal Switch |
|---|---|
| Pros | |
|
|
| Cons | |
|
|
Video: Patient Testimonial – Life after Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Weight Loss Surgery Alternative
Furthermore, after reviewing the risks and problems listed above that may result from a surgical procedure, you might be asking yourself, “What is the safest form of weight loss surgery?”
Even though laparoscopic surgery, like gastric sleeve, is considered minimally invasive. It also involves incisions and increases the risk. In addition, it brings with it a substantial recovery process and time frame.
There is a non-surgical procedure that can accomplish very close to the same results as gastric sleeve surgery. Moreover, this procedure is called Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) and is a cutting-edge procedure that has caught the attention of many surgeons over recent years.
Firstly, you can undergo ESG without requiring a hospital stay, incisions, or long recovery times. Moreover, ESG is a valuable tool when combined with diet and exercise, and can help higher-weight individuals lose between 60-70% of their excess weight in about 18 months.
To learn more about ESG contact IBI Healthcare Institute for a consultation today! We are here to help you select the best weight loss procedure and provide answers to all of your questions.











