Hernia Disease Overview
Hernia disease is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While they can be painful and uncomfortable, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage the condition effectively. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about hernias, from how they develop to the best ways to treat them.
What is a Hernia Disease?
Hernia disease is a common medical condition where an internal part of the body, typically a section of the intestine, pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or tissue wall. This causes a noticeable bulge that can lead to discomfort or pain. An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, pushes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. While hernias most often develop in the abdomen, they can also appear in the groin, upper thigh, and around the belly button. Globally, millions of people are affected by hernia disease each year.
According to the NIH, over 20 million hernia surgeries are performed worldwide annually. In the United States alone, more than 1 million hernia repairs are conducted each year, making it one of the most common surgical procedures.
What is the Main Cause of Hernia?
Hernia disease can result from a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Muscle weakness can be present at birth or develop later in life. Strain, on the other hand, can occur due to heavy lifting, persistent coughing, obesity, or even pregnancy. A combination of these factors can lead to the development of a hernia.
What Does a Hernia Feel Like?
At first, a hernia doesn’t cause any symptoms. But as it progresses you may feel a dull ache or discomfort in the area, especially when you lift, bend, or cough. Some people describe it as a feeling of heaviness or pressure.
What is Hernia Pain Like?
Hernia pain varies depending on the type and location of the hernia. It starts as a burning or aching sensation with mild discomfort and can get sharp when you do activities that put pressure on the abdomen like lifting heavy objects. For some, it can be severe pain, enough to affect daily activities.
What are the Symptoms of a Groin Hernia?
Inguinal hernias, the most common type of hernia in men, occur in the groin area. Symptoms of direct inguinal hernias are:
-
A bulge on one or both sides of the groin.
-
Pain or discomfort, when you bend, cough, or lift.
-
Heaviness or dragging sensation in the groin.
-
Weakness or pressure in the groin.
-
In men, pain and swelling around the testicles if the protruding intestine goes down to the scrotum.

Hernia Disease – Types and Differences
Hernia disease comes in several types or forms each with its characteristics:
-
Inguinal Hernia – The most common type occurs in the groin.
-
Femoral Hernia – Occurs in the groin area, specifically when tissue bulges through the lower abdomen into the upper thigh. More common in women.
-
Umbilical Hernia – Occurs near the belly button often seen in infants and individuals with higher body mass index.
-
Hiatal Hernia – Specifically, a hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity.
-
Incisional Hernia – Forms at the site of a previous surgical incision.
Inguinal and femoral hernias are conditions where organs protrude through muscle walls in the groin area. Treatment options include surgical interventions, which can vary in technique and invasiveness, with considerations for recovery and the choice between open hernia surgery and minimally invasive surgery.
What’s the Difference Between Inguinal and Pubic?
Inguinal hernia symptoms refer to the lower abdomen and pubic hernia symptoms refer to the lower area near the genital region. While they are close to each other, an inguinal hernia is in the lower abdomen and issues in the pubic area can be osteitis pubis or sports hernias.
What’s the Difference Between Inguinal and Hernia?
An inguinal hernia is a type of hernia in the inguinal region. Not all hernias are inguinal hernia surgery however, they can be in the upper thigh (femoral hernia), around the belly button (umbilical hernia), or even along surgical incisions (incisional hernia). The word, inguinal hernia diagnosis is a broad term that includes all of these.
Inguinal Hernia Location
The most inguinal hernias. area is the lower part of the abdomen that meets the thigh. Inguinal hernias occur when tissue pushes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall, usually in the symptoms of an inguinal canal which is a passage for the blood supply from vessels and nerves to the legs.
An indirect inguinal hernia is the most common type of inguinal hernia, often present at birth, and can develop in both sexes, although it is more prevalent in males due to anatomical differences.
Are Groin and Inguinal Hernias the Same?
Yes, groin hernias and inguinal hernias are interchangeable. Inguinal hernias refer to hernias in the groin area. Often confused by many due to the terms.
What Does a Ball Hernia Look Like?
A “ball hernia” is a visible bulge of abdominal tissue that forms when a hernia pushes through the abdominal wall. It’s a soft, round lump of abdominal ultrasound that can be pushed back in (reduced) when lying down but will come back out when standing or straining.
What Are The Risk Factors For A Hernia?
-
Age – Muscle weakness and tissue degeneration over time.
-
Gender – Men are more likely to have inguinal hernias.
-
Family History – Genetic predisposition.
-
Obesity – Extra weight on the abdominal muscles.
-
Chronic Cough – Persistent coughing from smoking or lung disease can weaken the abdominal wall.
-
Pregnancy – The growing uterus can cause pressure that leads to hernias.

Hernia Disease – Diagnosis and Self-Assessment
How Do I Check Myself for a Hernia?
Stand up and gently press around the area where you think you have a hernia. If you feel a bulge that gets bigger when you cough or strain, it might be a hernia. However, self-diagnosis is not a substitute for a medical evaluation.
What Can Be Mistaken for a Hernia?
-
Muscle Strain – Overuse can cause pain and swelling like a hernia.
-
Lymphadenopathy – Swollen lymph nodes in the groin can look like a hernia.
-
Testicular Conditions – Varicocele or hydrocele can cause swelling in the scrotum like an inguinal hernia.
How is a Hernia Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hernia by physical examination. They will ask you to stand, cough, or strain to make the hernia more visible. In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasound, CT, or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
What Imaging Tests are Used to Confirm a Hernia?
Imaging tests are used to confirm the presence and type of hernia:
-
Ultrasound – Used for groin hernias, especially in women and children.
-
CT – For complex or recurrent hernias.
-
MRI – For soft tissue detail to differentiate between hernias and other conditions.
Can You Have a Hernia Without Symptoms?
Yes, you can have a hernia without symptoms, especially in the early stages. Some hernias are only discovered during a physical exam or when complications arise from emergency surgery.
What Are the Early Warning Signs of an Inguinal Hernia?
Early signs of a hernia may be:
-
A small lump or bulge in the abdomen or groin.
-
Mild discomfort or pain that gets worse with activity.
-
The feeling of heaviness in the area.
When to See a Doctor for a Hernia?
See a doctor if you have a persistent bulge in your abdomen or groin, pain, or difficulty with daily activities due to discomfort. If an incarcerated hernia occurs, it becomes trapped in the abdominal wall and cannot be pushed back in, potentially leading to strangulation and severe complications. Immediate medical attention is necessary if the hernia becomes hard and tender or if you experience nausea and vomiting, as these could be signs of a strangulated hernia, which is a medical emergency.
How is a Hernia Different from Other Abdominal Conditions?
Hernias are different from other abdominal conditions like muscle strains or gastrointestinal issues in that they involve an actual protrusion of tissue through the abdominal wall. While other conditions may cause similar symptoms in internal organs like pain or swelling, hernias often have a visible or palpable bulge.
Hernia Disease – Treatment Options
How Do They Fix a Hernia?
Hernias are typically repaired through surgery, where the protruding scar tissue is pushed back into place, and the weakened area is reinforced. There are several surgical techniques, depending on the type and severity of the hernia.
What Is the Best Treatment for Groin Hernia?
The best treatment for a groin hernia, particularly an inguinal hernia, is usually surgical repair. Common inguinal hernia symptoms include discomfort when straining or lifting. It is important to track these symptoms, especially in relation to recovery after surgery and knowing when to seek medical attention. Options for direct inguinal hernia repair include:
-
Open Hernia Repair – The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia. Further pushes the bulging tissue back into place. Then reinforce the area with stitches or a synthetic mesh.
-
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair – In terms of treatment, laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure where the surgeon makes small incisions and uses a laparoscope to guide the surgical repair.
How Do You Fix a Groin Hernia?
Fixing a groin hernia typically involves surgery, as mentioned earlier. The specific approach depends on the hernia’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health. Because of this, laparoscopic hernia surgery is often preferred for its quicker recovery time and reduced post-operative pain.
How Do You Fix a Testicular Hernia?
A testicular hernia, or inguinal hernia that extends into the scrotum, is also treated with surgery. The procedure is similar to that of a standard, inguinal hernia surgery to repair but requires special care to avoid damage to the spermatic cord and blood vessels leading to the testicle.
Can You Repair a Hernia Without Surgery?
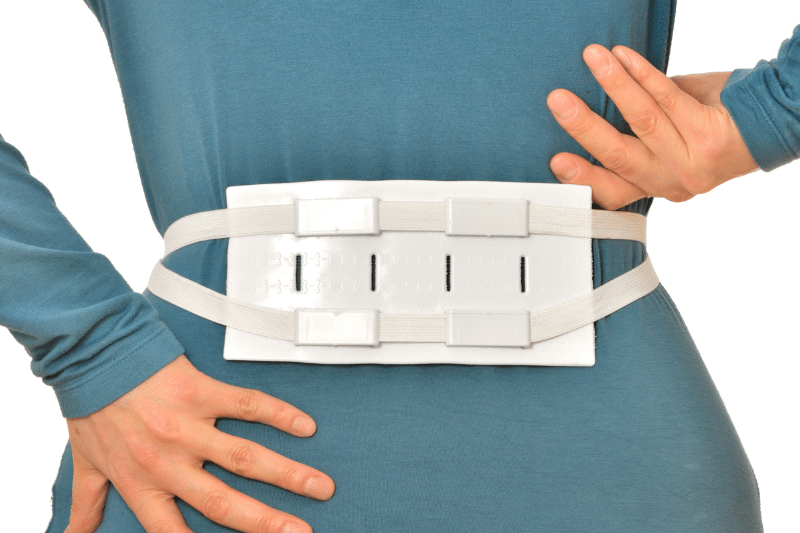
Some small or asymptomatic hernias can be managed without surgery. Doctors refer it to as “watchful waiting”. Moreover, non-surgical management might be lifestyle changes to reduce strain, wearing a truss or belt, and avoiding activities that make painful swelling around the hernia worse. However, doctors recommend surgery for symptomatic hernias to prevent complications.
Does a Groin Hernia Need Surgery?
Most groin hernias will need immediate surgery, especially if they are symptomatic or can become strangulated. Some may opt for nonsurgical management first but the risk of serious complications makes surgery the better option.
Can You Treat Testicular Hernia?
Yes, you can and should treat a testicular hernia, usually with surgery. Delaying treatment can lead to strangulation or testicular damage so timely treatment is important.
How Do You Get Rid of a Groin Hernia?
Getting rid of a groin hernia usually requires surgery. Furthermore, the procedure involves repairing the weak area of the abdominal wall and reinforcing it to prevent recurrence. Although, laparoscopic and open surgery are both options depending on the case.
What Are the Non-Surgical Options for Hernia Treatment?
Generally non-surgical options for hernia treatment limited. Particularly to lifestyle modifications and supportive devices. These might include:
-
Weight Management – Reducing obesity-related strain on the abdominal wall.
-
Exercise – Strengthening abdominal muscles to support weakened areas. Avoid lifting heavy weights.
-
Trusses or Belts – Wearing supportive devices to help keep the hernia in place.
-
Dietary Changes – Avoid foods that cause constipation or bloating, which can increase abdominal pressure.
How Does Laparoscopic Surgery Repair Hernias?
During laparoscopic abdominal surgery for hernia repair, the surgeon makes small incisions through the muscle wall of the abdominal cavity. Particularly with the laparoscope and surgical instruments. In addition, the surgeon uses these tools to repair the hernia and reinforce the abdominal wall with mesh. Nonetheless, this technique is less invasive than traditional open surgery and usually results in quicker recovery times.
What Are the Recovery Times for Different Hernia Surgeries?
Recovery times can vary based on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health:
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Typically, patients can return to light activities within 1-2 weeks and full activities, including exercise, within 4-6 weeks.
Open Hernia Repair
Recovery may take longer, with most patients resuming light activities in 2-4 weeks and full activities in 6-8 weeks.
Hernia Disease – Complications and Severity
How Serious is a Hernia in the Groin?
A groin hernia can range from mildly uncomfortable to a serious medical condition. If left untreated, it can lead to complications like incarceration (where the hernia becomes stuck in the protruded position) or strangulation (where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off). Regardless, both of them require emergency surgery.
Can a Hernia Be Life-Threatening?
While most hernias are not immediately life-threatening, they can become dangerous if complications like strangulation occur. Strangulation can cut off blood supply to the herniated tissue, leading to tissue death and potentially life-threatening infections.
Are Testicular Hernias Serious?
Testicular hernias, a type of inguinal hernia, can be serious if they are left untreated. The risk of complications like strangulation is present, and there is also the potential for testicular damage due to the pressure and strain on the spermatic cord.
What Happens If a Groin Hernia Is Left Untreated?
If a groin hernia is left untreated, it can lead to severe pain, increased size, and the potential for complications like incarceration or strangulation. Similarly, these complications are serious and can lead to emergencies requiring immediate surgery.
Can a Testicular Hernia Go Away on Its Own?
A testicular hernia will not go away on its own. The only way to repair the hernia is through surgery. While non-surgical management can alleviate symptoms temporarily, it will not resolve the hernia.
Will a Groin Hernia Heal Itself?
No, a groin hernia will not heal on its own. Surgical repair is usually necessary to correct the hernia and prevent complications.
What Are the Potential Complications of Untreated Hernias?
Untreated hernias can lead to several complications, including:
-
Incarceration – The hernia becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back in.
-
Strangulation – The blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off, leading to tissue death.
-
Bowel Intestinal Obstruction – A hernia can block the intestine, causing sudden pain and digestive issues.
How Does Hernia Surgery Impact Long-Term Health?
Hernia surgery can have a positive impact on long-term health by preventing complications and relieving symptoms. Most patients experience a significant improvement in their quality of life post-surgery, with reduced pain and discomfort. However, as with any surgery, there are risks, including infection, chronic pain, or hernia recurrence.
What Are the Risks of Hernia Recurrence?
Hernia recurrence is a potential risk after surgery. Factors that can increase this risk include:
-
Smoking – Delays healing and weakens tissue.
-
Obesity – Adds extra strain on the abdominal wall.
-
Heavy Lifting – Puts pressure on the repaired area.
-
Chronic Coughing – Weakens the abdominal muscles.
Using mesh reinforcement during abdominal surgery also has been shown to reduce the risk of recurrence.
How Do You Know If You Have A Hernia?
If you have a bulge or lump in your abdomen or groin, especially after lifting something heavy you might have a hernia. Consequently, pain, discomfort, or a dragging sensation are also symptoms. However, the only way to confirm a hernia is through a medical evaluation by a healthcare provider.
Hernia Disease – Managing Pain and Prevention
How to Relieve Hernia Pain in the Groin?
To relieve hernia pain in the groin:
-
Rest – Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
-
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers – Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
-
Supportive Wear – Trusses or hernia belts can provide relief by holding the hernia in place.
-
Ice Packs – Applying ice to the affected area can reduce inflammation and pain.
What Should You Not Do With a Groin Hernia?
If you have a groin hernia, you should avoid:
-
Heavy Lifting – This can worsen the hernia.
-
Straining During Bowel Movements – Constipation can increase abdominal pressure.
-
Intense Physical Activity – Activities that put strain on the abdominal muscles should be avoided.
How Painful is a Hernia?
A hernia can be painful from mild to very painful. Conversely, the level of pain depends on the size and location of the hernia and if it’s complicated by incarceration or strangulation.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Prevent Hernias?
Here are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent recurrent hernias:
-
Be Healthy Weight – Reduces strain on abdominal muscles.
-
Don’t Lift Heavy – If you have to lift, do it properly.
-
Stop Smoking – Smoking weakens connective tissues.
-
Exercise Regularly – Strengthen abdominal muscles without overstraining.
-
Eat a High Fiber Diet – Prevents constipation and reduces straining during bowel movement.
How Does Physical Activity Affect a Hernia?
Physical activity can help and hinder hernia management. Regular moderate exercise can strengthen abdominal muscles and overall health. But intense or improper exercise especially heavy lifting can worsen a hernia or increase the risk of recurrence after surgery.
What to Do if I Have a Hernia?
If you think you have a hernia, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications. Meanwhile, avoid activities that strain your abdomen and use supportive wear to manage symptoms.
What Exercises Should Be Avoided With a Hernia?
With a hernia, avoid exercises that put excessive strain on the abdominal muscles, such as:
-
Heavy Weightlifting – Especially squats, deadlifts, and bench presses.
-
Crunches and Sit-ups – These exercises can exacerbate the hernia.
-
High-Impact Activities – Running, jumping, or other high-impact sports can increase abdominal pressure.
How Can Diet and Weight Management Help Prevent Hernias?
A balanced diet rich in fiber can prevent constipation, reducing the risk of straining during bowel movements – a common cause of hernias. Maintaining a healthy weight also reduces the strain on the abdominal wall, lowering the risk of developing a hernia.
What Are the Best Practices for Managing Hernia Pain at Home?
Managing hernia pain at home involves several strategies:
-
Rest and Avoid Strain – Limit activities that exacerbate pain.
-
Use Pain Relievers – Over-the-counter medications can help.
-
Apply Ice or Heat – Depending on the pain, cold or warm compresses can provide relief.
-
Supportive Wear – Trusses or belts can help keep the hernia in place and reduce discomfort.











