Family planning methods play a vital role in helping individuals and couples control when and how many children they want. Among various options, tubal ligation stands out as a popular permanent birth control method. Conversely, some women may consider tubal ligation reversal to restore fertility when their family plans change.
This detailed guide will explore key aspects of family planning methods with a focus on tubal ligation and its reversal. We will cover eligibility, procedure details, risks, benefits, and what patients should expect.
What Are Family Planning Methods?
Before diving into tubal ligation and reversal, let’s briefly define family planning methods. These include various medical and non-medical techniques used to prevent or delay pregnancy. They help people plan and space pregnancies according to their desires and circumstances.
Family planning methods range from temporary options like condoms and oral contraceptives to permanent methods such as tubal ligation and vasectomy. These methods empower individuals to take control over their reproductive health, thus promoting healthier families and communities.
What Is Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that permanently prevents pregnancy by blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes. This stops eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus and prevents sperm from reaching the egg, thus avoiding fertilization.
Tubal ligation is often called “female sterilization” and is one of the most effective family planning methods for women who want a permanent form of birth control.
How Is Tubal Ligation Performed?
There are several techniques to perform tubal ligation:
- Laparoscopy: The most common method involves small incisions in the abdomen and, for example, the use of a camera and instruments to seal or cut the fallopian tubes.
- Mini-laparotomy: Usually done after childbirth, through a small incision near the bikini line to access the tubes.
- Hysteroscopic tubal ligation: A non-incisional procedure, in which devices are placed inside the fallopian tubes via the cervix to cause blockage.
Surgeons choose the method based on patient health, timing, and preference.
Benefits of Tubal Ligation as a Family Planning Method
- Highly effective: Tubal ligation has a failure rate of less than 1%, making it one of the most reliable birth control options.
- Permanent: Ideal for women who do not want more children.
- No hormones: Unlike some contraceptives, tubal ligation does not affect hormone levels.
- One-time procedure: Unlike daily pills or regular injections, it requires only one surgical intervention.
- Minimal impact on sexual function: Tubal ligation does not affect libido or menstrual cycles.
Risks and Considerations of Tubal Ligation
Like all surgeries, tubal ligation carries some risks:
- Infection or bleeding
- Damage to surrounding organs (rare)
- Possible failure leading to pregnancy (very rare)
- Ectopic pregnancy risk if failure occurs
It’s important to consider these factors and discuss them with your healthcare provider before choosing tubal ligation.
What Is Tubal Ligation Reversal?
Tubal ligation reversal is a surgical procedure that attempts to restore fertility by reconnecting the fallopian tubes that were previously blocked or cut. This procedure offers hope to women who have undergone tubal ligation but later wish to conceive.
However, tubal reversal is not always successful or suitable for everyone. Factors such as the method of tubal ligation, time since the procedure, and overall reproductive health affect outcomes.
How Is Tubal Ligation Reversal Performed?
Tubal reversal usually involves microsurgery under general anesthesia. Then, surgeons carefully remove damaged sections of the tubes and reconnect the healthy ends to restore the passage for eggs and sperm.
The procedure requires a skilled surgeon and can take several hours. Recovery times vary but generally include a few weeks of rest before normal activities.
Success Rates of Tubal Ligation Reversal
Success rates vary widely based on factors such as age, tubal damage, and surgical technique:
- Pregnancy rates after reversal range from 40% to 80%.
- Younger women and those with less tubal damage have higher chances.
- Some women may require assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like IVF if reversal fails.
Risks and Considerations of Tubal Ligation Reversal
- Infection or bleeding
- Damage to fallopian tubes
- Ectopic pregnancy risk remains higher than average
Given these risks, careful evaluation and counseling are essential.
Comparing Tubal Ligation and Reversal
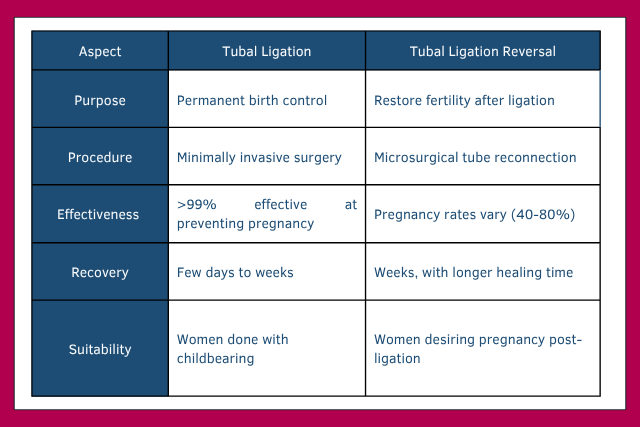
How to Decide Between Tubal Ligation and Reversal
Choosing the right family planning method requires understanding your goals, health, and circumstances. If you want permanent contraception, tubal ligation offers a reliable solution. However, if you later change your mind about having children, reversal is a complex but sometimes effective option.
Always consult a qualified provider to discuss the best approach tailored to your needs.
Alternatives to Tubal Ligation and Reversal
Not all women choose tubal ligation for family planning. Other options include:
- Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs): IUDs and implants offer effective, temporary contraception.
- Hormonal contraceptives: Pills, patches, and injections regulate fertility temporarily.
- Barrier methods: Condoms and diaphragms provide non-hormonal contraception.
- Vasectomy: A permanent method for male partners.
Understanding all options helps you make informed decisions.
Preparing for Tubal Ligation Surgery
Preparation involves:
- Medical evaluation and history review
- Counseling on permanent nature and alternatives
- Pre-surgery tests and fasting instructions
- Arranging support post-surgery
Recovery After Tubal Ligation
Recovery typically takes a few days to a week. You may experience:
- Mild pain or cramping
- Spotting or light bleeding
- Fatigue
Most women return to normal activities within a week but avoid heavy lifting for several weeks.
Preparing for Tubal Ligation Reversal Surgery
Before reversal, your doctor will:
- Assess your overall health and fertility status
- Perform imaging tests to check fallopian tubes
- Discuss realistic expectations
- Plan the surgical approach
Conclusion: Family Planning Methods – Tubal Ligation and Reversal
Family planning methods like tubal ligation and its reversal give women important options to control their fertility. Tubal ligation is a very effective permanent way to prevent pregnancy. Reversal can help women try to have children again, but only in certain cases.
In conclusion, knowing how these procedures work, their benefits, risks, and recovery helps women make smart choices that fit their goals. Always talk to skilled healthcare providers to get advice and care made just for you.










